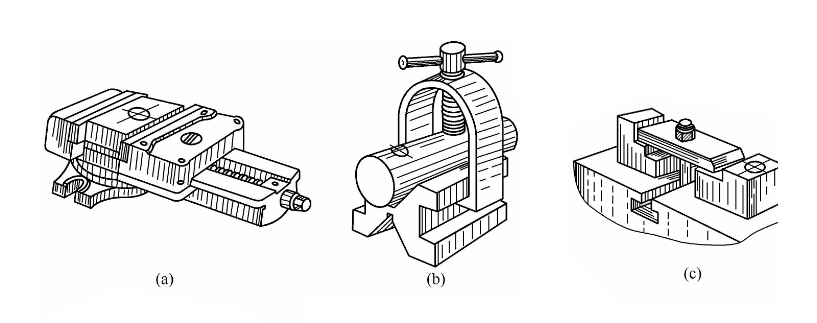
In order to ensure the quality and safety of drilling, different clamping methods should be adopted according to different shapes of workpieces and cutting forces.
(1) The workpiece with a flat shape can be clamped with a flat-jaw clamp, as shown in Figure (a).
(2) For cylindrical workpieces, V-shaped iron can be used for clamping, as shown in Figure (b).
However, the drill axis must be perpendicular to the symmetrical plane of V-shaped iron to avoid drilling asymmetry.
(3) When the diameter of the borehole is more than 12 mm, the larger workpiece can be drilled by the clamping method of pressure plate, as shown in Figure (c).
Matters needing attention:
- When clamping, the surface of the workpiece should be perpendicular to the axis of the drill bit.
- When the diameter of the borehole is less than 12 mm, the flat-jaw pliers can not be fixed. When the diameter of the borehole is larger than 12 mm, the flat-jaw pliers must be fixed.
- When drilling through holes of workpiece clamped by flat-mouth pliers, the bottom of workpiece should be padded with iron to empty out the hole position so as not to damage the flat-mouth pliers.